


Next: 3 Screening Protocol
Up: Flight X-ray CCD Selection
Previous: 1 Introduction
The ACIS instrument uses MIT Lincoln Laboratory CCID 17 Devices.[4]
These CCDs consist of a 1024 x 1026 pixel imaging section, with a separate 1024 x 1026
shielded frame store region. The pixels are 24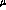 m square, and when coupled
with the focusing optics, will provide resolution of 0.5 arcseconds.
The frame store for these devices has a novel architecture, with two separate
sections that feed into two independent serial registers (see Figure 1).
This design permits charge to be clocked in either direction and
makes possible non-standard readout configurations. For example output nodes
A and B can be both be readout through output A, while nodes C and D are both
readout through C (AC mode).[4]
m square, and when coupled
with the focusing optics, will provide resolution of 0.5 arcseconds.
The frame store for these devices has a novel architecture, with two separate
sections that feed into two independent serial registers (see Figure 1).
This design permits charge to be clocked in either direction and
makes possible non-standard readout configurations. For example output nodes
A and B can be both be readout through output A, while nodes C and D are both
readout through C (AC mode).[4]
Both front-illuminated (incident photons pass through the gate structure)
and back-illuminated (incident photons incident directly into the
depleted silicon) devices have been made for ACIS. Back-illuminated
devices (BI) offer the advantage of higher quantum efficiency at lower
energies, but have significantly lower spectral resolution than the front-illuminated
(FI) devices.[5]
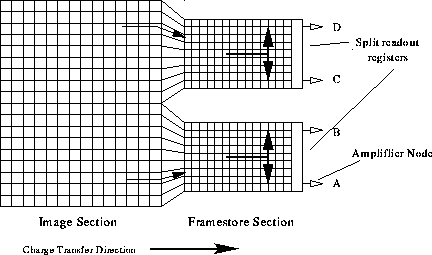
Figure 1: Schematic of CCID 17
mjp@space.mit.edu
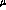 m square, and when coupled
with the focusing optics, will provide resolution of 0.5 arcseconds.
The frame store for these devices has a novel architecture, with two separate
sections that feed into two independent serial registers (see Figure 1).
This design permits charge to be clocked in either direction and
makes possible non-standard readout configurations. For example output nodes
A and B can be both be readout through output A, while nodes C and D are both
readout through C (AC mode).[4]
m square, and when coupled
with the focusing optics, will provide resolution of 0.5 arcseconds.
The frame store for these devices has a novel architecture, with two separate
sections that feed into two independent serial registers (see Figure 1).
This design permits charge to be clocked in either direction and
makes possible non-standard readout configurations. For example output nodes
A and B can be both be readout through output A, while nodes C and D are both
readout through C (AC mode).[4]
